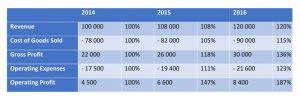
On the other hand, when a company generates surplus income, a portion of the long-term shareholders may expect some regular income in the form of dividends as a reward for putting their money into the company. Traders who look for short-term gains may also prefer dividend payments that offer instant gains. Profits give a lot of room to the business owner(s) or the company management to use the surplus money earned. This profit is often paid out to shareholders, but it can also be reinvested back into the company for growth purposes. The accountant credits retained earnings for $100,000, which increases equity.

How to Decrease Retained Earnings With Debit or Credit
And since expansion typically leads to higher profits and higher net income in the long-term, additional paid-in capital can have a positive impact on retained earnings, albeit an indirect impact. Retained earnings are affected by any increases or decreases in net income and dividends paid to shareholders. As a result, any items that drive net income higher or push it lower will ultimately affect retained earnings. Whether positive or negative, retained earnings appear at the top of the liabilities side of the balance sheet, as part of the company’sshareholders’ equity. Both revenue and retained earnings are important in evaluating a company’s financial health, but they highlight different aspects of the financial picture. Revenue sits at the top of the income statement and is often referred to as the top-line number when describing a company’s financial performance.
- It is an important component of a company’s financial statements, and understanding its role is essential for accountants, financial analysts, and business owners.
- Net income refers to the income for a period minus all the costs of doing business.
- In accounting, retained earnings is a permanent account, which means it is not closed at the end of each accounting period.
- Retained earnings refer to the net income of a company after it has paid dividends to its shareholders.
- A separate formal statement—the statement of retained earnings—discloses such changes.
- When preparing financial statements, the retained earnings from the trial balance are carried over to the equity section of the balance sheet.
How to Calculate Dividends, Retained Earnings and Statement of Cash Flow
Retained earnings show a credit balance and are recorded on the balance sheet of the company. According to this rule, an increase in retained earnings is credited and a decrease in retained earnings is debited. Adjustments to retained earnings are made by first calculating the amount that needs adjustment. Next, the amount deducted from your retained earnings is recorded as a line item on your balance sheet. When a company issues common and preferred stock, the value investors pay for that stock is called paid-in capital. The amount of this capital is equal to the amount the investor pays for the stock in addition to the face Food Truck Accounting value of the share itself.
- At the end of an accounting year, the balances in a corporation’s revenue, gain, expense, and loss accounts are used to compute the year’s net income.
- In essence, Retained Earnings represents the accumulated profits that a company has kept over time.
- This analysis can reveal insights into a company’s operational efficiency, profitability, and the effectiveness of its reinvestment strategies.
- Retained earnings is the cumulative amount of earnings since the corporation was formed minus the cumulative amount of dividends that were declared.
What is the Normal Balance in the Retained Earnings Account?

Retained earnings is a crucial component of a company’s financial statements, representing the portion of profits that are reinvested in the business rather than being distributed to shareholders as dividends. Understanding whether retained earnings is a debit or credit is essential for accurate financial reporting and analysis. In this article, we will delve into the concept of retained earnings and explore whether it is a debit or credit. The trial balance serves as a foundational report in the accounting process, providing a snapshot of all account balances at a given point in time, including retained earnings.
Management and Retained Earnings
Positive earnings are more commonly referred to as profits, while negative earnings are more commonly referred to as losses. The retained earnings normal balance is the money a company has after calculating its net income and dispersing dividends. For example, management might decide to build up a cash reserve, repay debt, fund strategic investment projects or pay dividends to shareholders. A company with consistently mounting retained earnings signals that it’s profitable and reinvesting in the business. Conversely, consistent decreases retained earnings is debit or credit in retained earnings may indicate mounting losses or excessive payouts to owners. The amount of a corporation’s retained earnings is reported as a separate line within the stockholders’ equity section of the balance sheet.

This report ensures that debits and credits are accurately recorded and balanced, which is a preliminary step before compiling more detailed financial statements. Retained earnings appear on the trial balance as part of equity and represent the link between the income statement and the balance sheet. They reflect the residual net income after accounting for any dividends distributed to shareholders.
- For example, a change in consumer behavior might necessitate increased marketing spend, affecting both net income and retained earnings.
- All of the other options retain the earnings for use within the business, and such investments and funding activities constitute retained earnings.
- If a company’s earnings are negative, the company has incurred losses from its operations.
- Find out how it sheds light on your company’s financial management, with a case study to illustrate.
- Since retained earnings are a part of shareholders’ equity, it is an obligation of the company to pay it back to the owners.
Retained Earnings Versus Dividends
Whenever a company declares distributions, the amount used to pay the shareholder dividends is deducted from the retained earnings account. Hence, retained earnings are the portion of a company’s net income that is set aside by the company for various operational purposes after dividend payments to its shareholders. If a company’s earnings are positive, it means the company has been able to generate profits from the goods and services they offer.
HP Inc. earned a net profit of 500,000 during the accounting period Jan-Dec 20×1. The company decided to retain the earnings for that year and utilize them for further growth. This is a liability (shareholders’ fund) of the company to pay the earnings back to the shareholders. Samsung Inc. earned a net profit of 500,000 during the accounting period Jan-Dec 20×1. The company Online Accounting decided to retain the profits for that year and invest the retained earnings in expanding the business. Retained earnings are a company’s cumulative earnings since its inception after the subtraction of the cumulative amount that has been paid out as dividends to shareholders.


